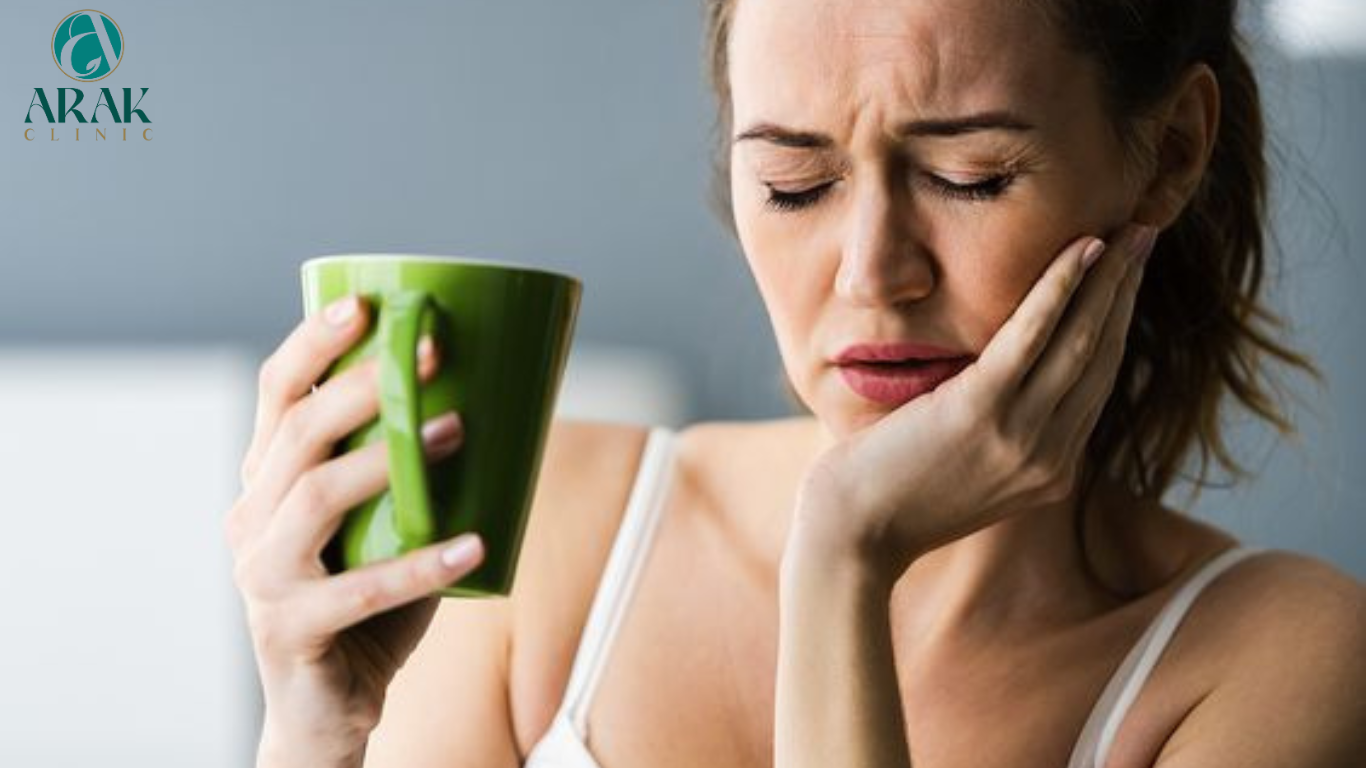
Toothaches can be caused by various dental and oral health issues. Common causes of toothache include:
Tooth Decay (Cavities): One of the most common causes of toothache is tooth decay. Bacteria in the mouth produce acid that can erode tooth enamel, leading to the formation of cavities. Cavities can expose the sensitive inner layers of the tooth, causing pain and sensitivity.
Gum Disease: Advanced gum disease (periodontitis) can lead to gum recession, exposing the tooth roots. This can result in tooth sensitivity and pain, especially when eating or drinking hot or cold substances.
Tooth Abscess: A tooth abscess is a painful infection that forms at the root of a tooth or in the space between the teeth and gums. It can cause intense throbbing pain, swelling, and fever.
Tooth Fractures or Cracks: Cracked or fractured teeth can be extremely painful, especially when biting or chewing. The severity of the pain depends on the extent of the fracture.
Tooth Sensitivity: Tooth sensitivity can cause a sharp, temporary pain when exposed to hot or cold temperatures, sweet or acidic foods, or air. It is often due to exposed dentin, which is more sensitive than enamel.
Dental Fillings: Occasionally, dental fillings can become loose or damaged, leading to tooth sensitivity and pain. This is more common with older fillings.
Bruxism (Teeth Grinding): Habitual teeth grinding or clenching, especially at night, can lead to toothaches, jaw pain, and headaches.
Impacted Wisdom Teeth: Impacted wisdom teeth, which do not fully emerge from the gums, can cause pain and discomfort in the back of the mouth.
Orthodontic Braces or Appliances: Braces, wires, or orthodontic appliances can sometimes cause discomfort or soreness, especially after adjustments.
Sinus Infections: Sinus infections (sinusitis) can cause referred pain to the upper rear teeth, mimicking a toothache.
Trauma or Injury: A direct blow to the mouth or face can result in broken teeth or damaged dental structures, leading to toothache.
Erupting Teeth: In children and teenagers, the eruption of new teeth, such as molars or wisdom teeth, can cause temporary discomfort and pain.
Other Medical Conditions: In some cases, toothache may be a symptom of underlying medical conditions like ear infections or heart problems, although these instances are less common.
Ignoring a toothache can lead to more severe dental problems and complications, so seeking timely dental care is crucial to relieve pain and maintain oral health.