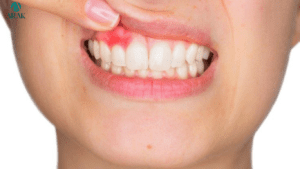
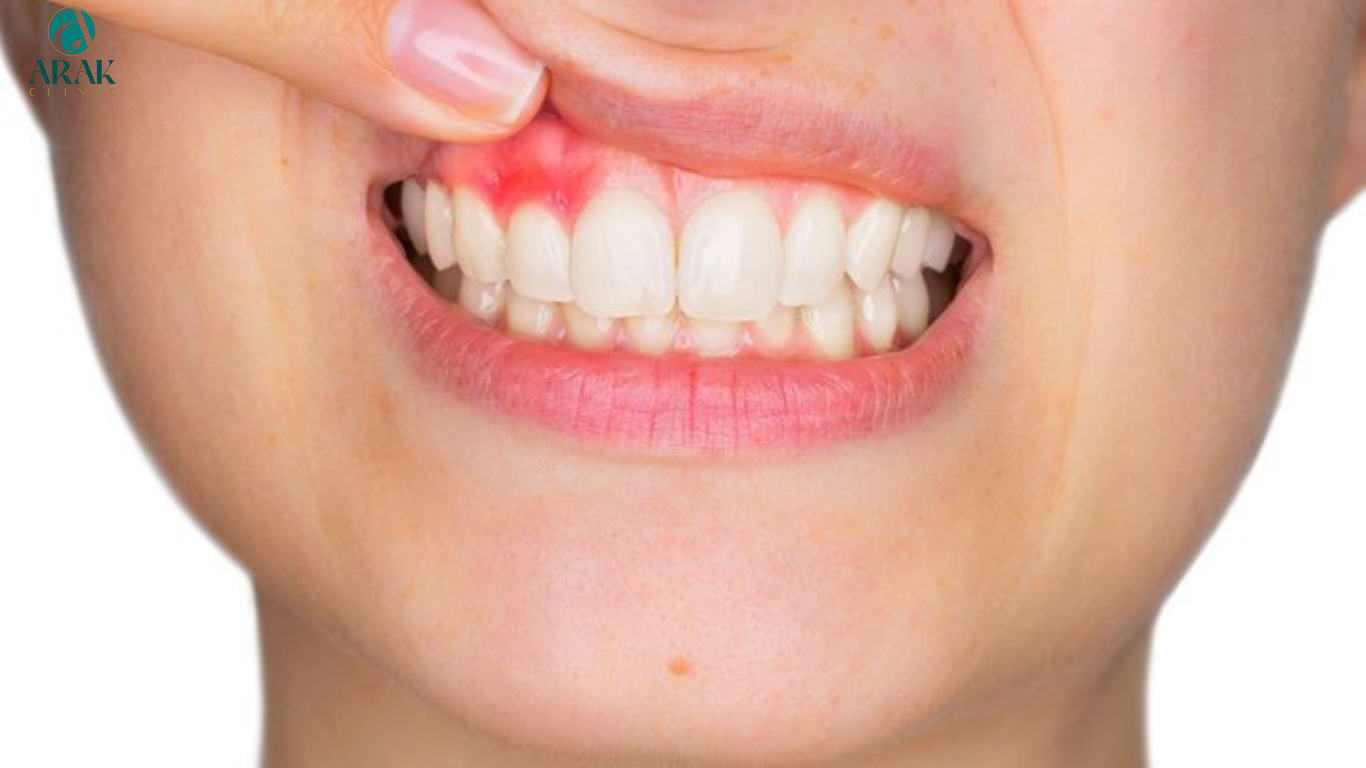
Gum recession is a common dental condition that occurs when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth wears away or pulls back, exposing the tooth roots. While it can lead to aesthetic concerns and tooth sensitivity, untreated gum recession may also result in more severe dental issues, such as tooth decay and tooth loss. Understanding the causes, treatment options, and preventive measures for gum recession is crucial for maintaining optimal oral health. Let’s delve into the factors contributing to gum recession, available treatments, and strategies for preventing its progression.
Causes of Gum Recession:
Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing, flossing, and regular dental cleanings can allow plaque and tartar buildup along the gumline, leading to gum disease and eventual recession.
Gum Disease: Advanced stages of gum disease, such as periodontitis, can cause gum tissue to deteriorate and recede, exposing tooth roots and increasing the risk of tooth loss.
Aggressive Brushing: Brushing teeth too hard or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can contribute to gum recession by wearing down the gum tissue over time.
Tooth Misalignment: Crooked or misaligned teeth can place uneven pressure on the gums, causing them to recede in certain areas.
Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as those occurring during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, can make gum tissue more susceptible to recession.
Tobacco Use: Smoking or chewing tobacco can impair blood flow to the gums, weaken gum tissue, and increase the risk of gum recession.
Genetics: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to gum recession, making them more prone to developing the condition regardless of their oral hygiene habits.
Treatment Options for Gum Recession:
Scaling and Root Planing: Deep cleaning procedures can remove plaque and tartar buildup from below the gumline and smooth out rough tooth surfaces to promote gum reattachment.
Gum Grafting: In cases of advanced gum recession, gum tissue grafts may be performed to cover exposed tooth roots and restore gum tissue volume.
Pinhole Surgical Technique (PST): A minimally invasive procedure that involves making small holes in the gum tissue and gently repositioning it over exposed tooth roots to treat gum recession.
Periodontal Surgery: Surgical techniques such as flap surgery or guided tissue regeneration may be recommended for severe cases of gum recession to regenerate lost gum tissue and bone support.
Preventive Measures for Gum Recession:
Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brush teeth twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush, floss daily, and schedule regular dental check-ups and cleanings.
Use a Gentle Brushing Technique: Avoid aggressive brushing and use gentle, circular motions to clean teeth and gums effectively.
Quit Smoking: Quitting smoking and avoiding tobacco products can improve gum health and reduce the risk of gum disease and recession.
Address Tooth Misalignment: Correcting misaligned teeth through orthodontic treatment can alleviate uneven pressure on the gums and prevent recession.
Manage Hormonal Changes: Maintain overall health and address hormonal imbalances with the guidance of healthcare professionals during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause.
Protect Teeth During Sports: Wear a mouthguard during sports activities to prevent trauma to the teeth and gums that may contribute to gum recession.
At Arak Clinic, our experienced dental team provides comprehensive care for gum recession, including diagnosis, treatment, and preventive strategies tailored to each patient’s unique needs. We are committed to helping our patients achieve and maintain healthy gums and smiles for life.